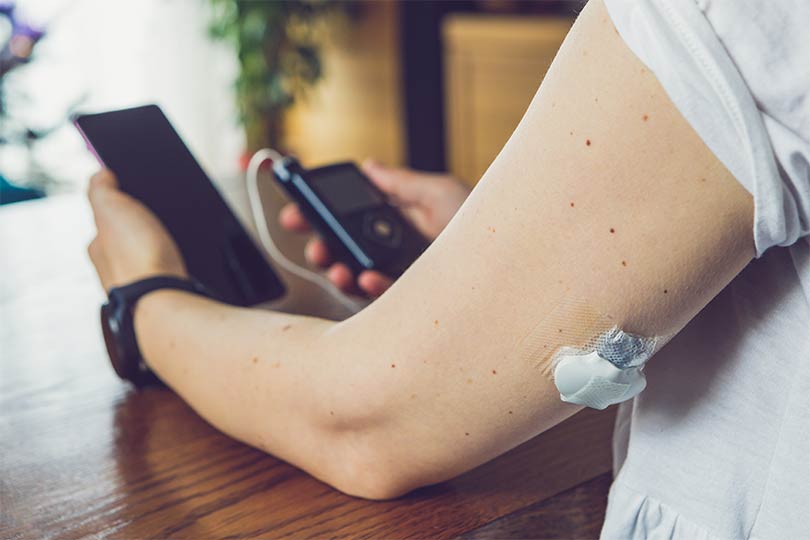
What is a continuous glucose monitor?
A CGM is a wearable device that helps track your glucose levels within interstitial fluid throughout the day and night. It works by inserting a tiny sensor just beneath your skin, where it measures glucose levels in your interstitial fluid—the watery substance that surrounds your body's cells and tissues. The glucose level in interstitial fluid is not quite the same as in our blood, but it is a good indicator of your blood glucose status.
The sensor connects to a transmitter that sends your glucose readings to either a smartphone app, a handheld device or an insulin pump. It’s also possible to share your CGM readings directly with your healthcare provider to help improve diabetes management. Depending on the type of CGM you choose, you might receive automatic updates or need to manually scan the sensor for readings. Some CGMs may require periodic finger-stick calibrations for accuracy. Most CGM sensors last for approximately 1-2 weeks before requiring replacement, making them a convenient option for ongoing monitoring.
Benefits of using a CGM
CGMs offer several advantages that can make managing diabetes easier and more effective:
- Real-time food insights: You can see how different foods affect your blood sugar levels immediately, helping you make better dietary choices
- Better carb counting: For people who take mealtime insulin, CGMs make it easier to match insulin doses with carbohydrate intake
- Medication management: You can better understand how your diabetes medications impact your blood sugar levels throughout the day
- Exercise tracking: CGMs show you how physical activity affects your glucose levels, helping you plan workouts more effectively
- Automated insulin delivery: Some CGMs can communicate with insulin pumps to automatically adjust insulin doses based on your readings
How can I get a CGM?
Most CGMs require a prescription, but some newer models are available over the counter. Use care and consult a healthcare provider when considering over-the-counter CGMs, as not all of them are cleared for use in people with diabetes.
How to know if a CGM is right for you: Test your blood sugar levels
If you're unsure whether you have diabetes but are considering a CGM, start by talking to your healthcare provider about getting an HbA1c test, which measures your average blood sugar levels over an extended period to help screen for prediabetes and diabetes. Labcorp OnDemand’s Diabetes Risk (HbA1c) Test measures your average blood sugar levels over 8-12 weeks to assess your risk of diabetes.
If you have diabetes, Labcorp OnDemand's Diabetes Management Test can help you and your healthcare provider plan lifestyle and diet changes accordingly, including potential use of a CGM to help monitor blood sugar levels.
As technology continues to advance, CGMs are making it easier than ever to manage diabetes effectively. By providing continuous data about your blood sugar levels, these devices can help you make more informed decisions about your diet, exercise and medication management.
Remember, the key to successful diabetes management is working closely with your healthcare team to find the right monitoring approach for your specific needs. Whether you choose a traditional glucometer or a CGM, staying informed about your blood sugar levels is an essential step in maintaining your health.